Flibanserin, girosa
167933-07-5 cas no
147359-76-0 (monoHCl)
Raleigh, N.C., December 11, 2013 – Sprout Pharmaceuticals today announced that it has received and appealed the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) Complete Response Letter (CRL) for flibanserin through the Formal Dispute Resolution process. Flibanserin is an investigational, once-daily treatment for Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder, or HSDD, in premenopausal women. HSDD is the most commonly reported form of female sexual dysfunction
read all here
A new drug being developed by Boehringer Ingelheim could give a boost to the sex drive of women with low libido. The drug, known as flibanserin, has been shown in clinical trials to increase their sexual desire when taken once a day at bedtime.
The results from four pivotal Phase III clinical trials on women with hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) were presented this week at the European Society for Sexual Medicine’s congress in Lyon, France. The trials showed that participants taking flibanserin had a significant improvement in their sexual desire compared to those given a placebo. They also experienced less of the distress associated with sexual dysfunction.
The drug was initially being investigated as a treatment for depression, and acts on the serotonin receptors in the brain – it is both a 5-HT1A receptor agonist and a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist. It is also a partial agonist at the dopamine D4 receptor.

Neurotransmitters such as serotonin are believed to be involved in sexual function, and antidepressants are commonly associated with a loss of libido, so this was an obvious side-effect to look out for during clinical trials in depression. But far from suppressing the libido in women, it appeared to have the opposite effect, so trials in women with HSDD were initiated.
Hormone replacement can improve the libido of women who have had their ovaries removed, but there is no available drug to treat those who have not. There have been accusations that pharma companies invent new diseases like HSDD in order to sell more medicines, but according to Kathleen Segraves, an assistant professor at Case Western Reserve University in the US who has worked in the field of sexual functioning for many years, this is not the case here. HSDD is a very real disorder, she says, and the potential for a treatment for these women is very exciting.

Flibanserin (code name BIMT-17; proposed trade name Girosa) is a drug that was investigated by Boehringer Ingelheim as a novel, non-hormonal treatment for pre-menopausal women with Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder (HSDD).[1][2] Development was terminated in October 2010 following a negative report by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.[3]
HSDD is the most commonly reported female sexual complaint and characterized by a decrease in sexual desire that causes marked personal distress and/or personal difficulties. According to prevalence studies about 1 in 10 women reported low sexual desire with associated distress, which may be HSDD.[4] The neurobiological pathway of female sexual desire involves interactions among multiple neurotransmitters, sex hormones and various psychosocial factors. Sexual desire is modulated in distinct brain areas by a balance between inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters, serotonin acting as an inhibitor while dopamine and norepinephrine act as a stimulator of sexual desire.[5][6]Flibanserin is a 5-HT1A receptor agonist and 5-HT2A receptor antagonist that had initially been investigated as an antidepressant. Preclinical evidence suggested that flibanserin targets these receptors preferentially in selective brain areas and helps to restore a balance between these inhibitory and excitatory effects.[6] HSDD has been recognized as a distinct sexual function disorder for more than 30 years.
The proposed mechanism of action refers back to the Kinsey dual control model. Several sex steroids, neurotransmitters, and hormones have important excitatory or inhibitory effects on the sexual response. Among the neurotransmitters, the excitatory activity is driven by dopamine and norepinephrine, while the inhibitory activity is driven by serotonin. The balance between these systems is relevant for a healthy sexual response. By modulating these neurotransmitters in selective brain areas, flibanserin, a 5-HT1A receptoragonist and 5-HT2A receptor antagonist, is likely to restore the balance between these neurotransmitter systems.[6]
Several large pivotal Phase III studies with Flibanserin were conducted in the USA, Canada and Europe. They involved more than 5,000 pre-menopausal women with generalized acquired Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder (HSDD). The results of the Phase III North American Trials demonstrated that
Although the two North American trials that used the flibanserin 100 mg qhs dose showed a statistically significant difference between flibanserin and placebo for the endpoint of [satisfying sexual events], they both failed to demonstrate a statistically significant improvement on the co-primary endpoint of sexual desire. Therefore, neither study met the agreed-upon criteria for success in establishing the efficacy of flibanserin for the treatment of [Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder].
These data were first presented on November 16, 2009 at the congress of the European Society for Sexual Medicine in Lyon, France. The women receiving Flibanserin reported that the average number of times they had “satisfying sexual events” rose from 2.8 to 4.5 times a month. However, women receiving placebo reported also an increase of “satisfying sexual events” from 2.7 to 3.7 times a month. Evaluation of the overall improvement of their condition and whether the benefit was meaningful to the women, showed a significantly higher rate of a meaningful benefit in the flibanserin-treated patient group versus the placebo group.The onset of the Flibanserin effect was seen from the first timepoint measured after 4 weeks of treatment and maintained throughout the treatment period.The overall incidence of adverse events among women taking flibanserin was low, the majority of adverse events being mild to moderate and resolved during the treatment. The most commonly reported adverse events included dizziness, nausea, fatigue, somnolence and insomnia.
On June 18, 2010, a federal advisory panel to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) unanimously voted against recommending approval of Flibanserin. Earlier in the week, a FDA staff report also recommended non-approval of the drug. While the FDA still might approve Flibanserin, in the past, negative panel votes tended to cause the FDA not to approve.
On October 8, 2010, Boehringer Ingelheim announced that it would discontinue its development of flibanserin in light of the FDA advisory panel’s recommendation.
On June 27, 2013, Sprout Pharmaceuticals confirmed they had resubmitted flibanserin for FDA approval.
- Borsini F, Evans K, Jason K, Rohde F, Alexander B, Pollentier S (summer 2002). “Pharmacology of flibanserin”. CNS Drug Rev. 8 (2): 117–142. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2002.tb00219.x. PMID 12177684.
- Jolly E, Clayton A, Thorp J, Lewis-D’Agostino D, Wunderlich G, Lesko L (April 2008). “Design of Phase III pivotal trials of flibanserin in female Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder (HSDD)”. Sexologies 17 (Suppl 1): S133–4. doi:10.1016/S1158-1360(08)72886-X.
- Spiegel online: Pharmakonzern stoppt Lustpille für die Frau, 8 October 2010 (in German)
- Nygaard I (November 2008). “Sexual dysfunction prevalence rates: marketing or real?”. Obstet Gynecol 112 (5): 968–9.doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000335775.68187.b2. PMID 18978094.
- Clayton AH (July 2010). “The pathophysiology of hypoactive sexual desire disorder in women”. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 110 (1): 7–11.doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2010.02.014. PMID 20434725.
- Pfaus JG (June 2009). “Pathways of sexual desire”. J Sex Med 6 (6): 1506–33. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01309.x.PMID 19453889.
- Yves Aubert, Thesis, Leiden University. (Dec 11, 2012) Sex, aggression and pair-bond: a study on the serotonergic regulation of female sexual function in the marmoset monkey
- Viagra for women?
- Marazziti D, Palego L, Giromella A, et al. (June 2002). “Region-dependent effects of flibanserin and buspirone on adenylyl cyclase activity in the human brain”. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 5 (2): 131–40. doi:10.1017/S1461145702002869.PMID 12135537.
- Podhorna J, Brown RE (June 2000). “Flibanserin has anxiolytic effects without locomotor side effects in the infant rat ultrasonic vocalization model of anxiety”. Br J Pharmacol 130 (4): 739–746. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0703364. PMC 1572126.PMID 10864879.
- Brambilla A, Baschirotto A, Grippa N, Borsini F (December 1999). “Effect of flibanserin (BIMT 17), fluoxetine, 8-OH-DPAT and buspirone on serotonin synthesis in rat brain”. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 10 (1): 63–7. doi:10.1016/S0924-977X(99)00056-5.PMID 10647099.
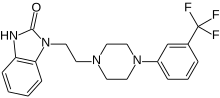
The compound 1-[2-(4-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3-dihydro-1 H- benzimidazol-2-one (flibanserin) is disclosed in form of its hydrochlorid in European Patent Application EP-A-526434 and has the following chemical structure:
Flibanserin shows affinity for the 5-HTιA and 5-HT2-receptor. It is therefore a promising therapeutic agent for the treatment of a variety of diseases, for instance depression, schizophrenia, Parkinson, anxiety, sleep disturbances, sexual and mental disorders and age associated memory impairment.

EXAMPLE
375 kg of 1-[(3-trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-(2-cloroethyl)piperazin are charged in a reactor with 2500 kg of water and 200 kg of aqueous Sodium Hydroxide 45%. Under stirring 169.2 kg of 1-(2-propenyl)-1,3-dihydro-benzimidazol-2H-one, 780 kg of isopropanol, 2000 kg of water and 220 kg of aqueous Sodium Hydroxide 45% are added. The reaction mixture is heated to 75-85° C. and 160 kg of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 200 kg of water are added. The reaction mixture is stirred at constant temperature for about 45 minutes. After distillation of a mixture of water and Isopropanol (about 3000 kg) the remaining residue is cooled to about 65-75° C. and the pH is adjusted to 6.5-7.5 by addition of 125 kg of aqueous Sodium Hydroxide 45%. After cooling to a temperature of 45-50° C., the pH value is adjusted to 8-9 by addition of about 4 kg of aqueous Sodium Hydroxide 45%. Subsequently the mixture is cooled to 30-35° C. and centrifuged. The residue thus obtained is washed with 340 l of water and 126 l of isopropanol and then with water until chlorides elimination. The wet product is dried under vacuum at a temperature of about 45-55° C. which leads to 358 kg of crude flibanserin polymorph A. The crude product thus obtained is loaded in a reactor with 1750 kg of Acetone and the resulting mixture is heated under stirring until reflux. The obtained solution is filtered and the filtrate is concentrated by distillation. The temperature is maintained for about 1 hour 0-5° C., then the precipitate solid is isolated by filtration and dried at 55° C. for at least 12 hours.
The final yield is 280 kg of pure flibanserin polymorph A.
Flibanserin may be prepared by reacting 1-(phenylvinyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzimidazol-2-one (I) with 1,2-dichloroethane (II) in the presence of NaH in warm dimethylformamide. The resulting 1-(2-chloroethyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzimidazol-one (III) is in turn coupled with commercially available m-trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine hydrochloride (IV) in the presence of sodium carbonate and catalytic potassium iodide in refluxing ethanol. The crude flibanserin hydrochloride (V) is then dissolved in aqueous ethanol and the pure base is precipitated upon addition of sodium hydroxide.
…………………………
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, v.57, 2012 Jan 5, p.104(5)
Isolation and structural elucidation of flibanserin as an adulterant in a health supplement used for female sexual performance enhancement
Low, Min-Yong et al
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0731708511004833
This proposed formula and structure was further confirmed by 1
H and 13C NMR data which indicated the presence of 20 carbon atoms and 21 protons.
proton nmr
13 c nmr
1D and 2DNMR data were used to assign the protons and carbon atoms.
In the1H NMR spectrum , a sharp singlet at 10.00 ppm integrating for one
proton is a typical proton attached to nitrogen. HMBC correlated this proton to C-2, C-4, and C-9 suggesting that it was H-3.
Complex signals were observedbetween 7.00 to 7.31 ppm, integrating for eight protons. A triplet at 7.31 ppm,integrating for a proton has a coupling constant of 8.0 Hz. HMBC correlated thisproton with C-16, C-19, and C-21 suggesting that it was H-20.
A double-doubletsplitting pattern at chemical shift 7.11 ppm, integrating for a proton, has couplingconstants of 6.3 Hz and 1.6 Hz.
HMBC correlated this proton to C-6, C-7, and C-9 showing that it was H-8. Overlapped signals were observed from 7.04 ppm to7.10 ppm, integrating for five protons. A double-doublet splitting pattern at 7.01ppm with coupling constant 8.0 Hz and 2.0 Hz, integrating for a proton was
observed.
HMBC correlated this proton to C-17 suggesting that it was either H-19or H-21. Four triplet signals were also observed from 2.73 ppm to 4.08 ppm,integrating for a total of twelve protons.
Two of these triplet signals at 2.74 ppmand 3.22 ppm integrated for four protons each, suggesting overlapping signals ofmethylene protons. This was further confirmed by 13C and DEPT NMR.
13C and DEPT NMR data showed the signals of four methylene, eight methineand six quaternary carbon atoms. The DEPT signals at 53.1 ppm and 48.6 ppmhave intensities which were double of those from the rest of the methylene carbonsignals, suggesting two methylene carbon atoms each contributing to the signal at 53.1 ppm and 48.6 ppm.
HMQC results further indicated that these two methylene carbon signals at 53.1 ppm and 48.6 ppm were correlated to the protons signal at 2.73 ppm and 4.08 ppm respectively, which corresponded to four protons each. The finding confirmed overlapping methylene carbon signals (at 53.1 ppm and 48.6 ppm) and methylene proton signals (at 2.73 ppm and 4.08 ppm). Hence, the unknown compound has six methylene carbon atoms with a total of twelve methylene protons.
The chemical shifts of the twelve methylene protons suggested that they were attached to relatively electronegative atoms. It was speculated that the six methylene groups were attached to the nitrogen atoms and the electron withdrawing effect of these electronegative nitrogen atoms resulted in the deshielding of the protons. HMBC and COSY correlations were used to assign the rest of the protons
The 13C NMR data showed that there were two quaternary carbon at
155.6 ppm and 151.3 ppm. The carbon with chemical shift 155.6 ppm was C-2. Inthe structure of imidazolone, carbonyl carbon C-2 was attached to two nitrogenatoms which helped to withdraw electrons from oxygen to C-2. Hence, C-2 wasless deshielded as compared to a normal carbonyl carbon which has chemical shiftabove 170 ppm.
Eight methine carbons and two quaternary carbons with chemicalshifts above 108 ppm suggested the presence of two aromatic rings. Thequaternary carbon with chemical shift 125.4 ppm was C-22 which was attached tothree fluorine atoms. Due to the strong electron withdrawing effect of the fluorineatoms, C-22 was highly deshielded and had a high chemical shift.
The IR spectrum of the isolated compound showed absorption bands of amide (νC=O 1685 cm-1, νN-H (stretch) 3180 cm-1, νN-H (bending) 1610 cm-1), alkyl fluoride (νC-F1077 cm-1, 1112 cm-1, 1158 cm-1), aromatic ring (ν Ar-H 3028 cm-1, 3078 cm-1 andνC=C 1401 cm-1, 1446 cm-1, 1453 cm-1, 1468 cm-1, 1487 cm-1) and alkane (νC-H2891 cm-1, 2930 cm-1 2948 cm-).
The IR spectrum supported the structure of
flibanserin.
……………………………….
US5576318, 1996
1 H NMR (DMSO-d6 /CDCL3 5:2) 11.09 (b, 1H), 11.04 (s, 1H), 7.5-6.9 (SH), 4.36 (t, 2H), 4.1-3.1 (10 H)
Filed under: New Drug Application Resubmission FDA, Uncategorized Tagged: anthony crasto, drugs, Flibanserin, medicinal chemistry, NEW DRUGS, organic chemistry, world drug tracker