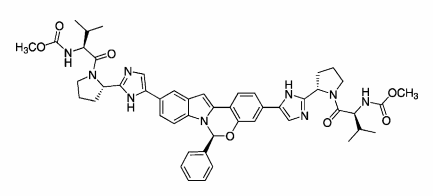
Elbasvir, MK 8742
1370468-36-2 cas
methyl N-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[4-[(6S)-3-[2-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-4H-imidazol-4-yl]-6-phenyl-6H-indolo[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazin-10-yl]-2H-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate
Methyl [(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[4-[(6S)-3-[2-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-1H-imidazol-4-yl]-6-phenylindolo[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazin-10-yl]-1H-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate
Carbamic acid, N,N‘-[[(6S)-6-phenyl-6H-indolo[1,2-c][1,3]benzoxazine-3,10-diyl]bis[1H-imidazole-5,2-diyl-(2S)-2,1-pyrrolidinediyl[(1S)-1-(1-methylethyl)-2-oxo-2,1-ethanediyl]]]bis-, C,C‘-dimethyl ester
Carbamic acid, N,N’-(((6S)-6-phenyl-6H-indolo(1,2-c)(1,3)benzoxazine-3,10-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-5,2-diyl-(2S)-2,1-pyrrolidinediyl((1S)-1-(1-methylethyl)-2-oxo-2,1-ethanediyl)))bis-, C,C’-dimethyl ester
Dimethyl N,N’-(((6S)-6-phenylindolo(1,2-c)(1,3)benzoxazine-3,10-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-5,2-diyl-(2S)-pyrrolidine-2,1-diyl((2S)-3-methyl-1-oxobutane-1,2-diyl)))dicarbamate
Methyl ((1S)-1-(((2S)-2-(4-((6S)-10-(2-((2S)-1-((2S)-2-((methoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-methylbutanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl)-1H-imidazol-4-yl)-6-phenyl-6H-indolo(1,2-c)(1,3)benzoxazin-3-yl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)carbonyl)-2-methylpropyl)carbamate
MW 882.0171, C49 H55 N9 O7,
UNII-632L571YDK
MERCK-PHASE 2
HCV NS5A Inhibitors
patent….http://www.google.com/patents/WO2012040923A1?cl=en
MK-8742 is in phase II clinical development at Merck & Co. for the oral treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection in combination with MK-5172 and ribavirin. Phase I clinical trials are uongoing for the treatment of hepatitis C infected males. In 2013, breakthrough therapy designation was assigned to the compound.
MK-8742 is an inhibitor of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) non-structural protein 5A (NS5A) that is being developed for the treatment of HCV infection. MK-8742 has broad, potent HCV genotypic activity in vitro against viral variants that are resistant to other NS5A inhibitors. MK-8742 exhibits potent antiviral activity during 5 days of monotherapy in patients with GT1 and GT3 chronic HCV infection. MK-8742 is currently in Phase IIB development.


MK-8742 is an inhibitor of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) non-structural protein 5A (NS5A) that is being developed for the treatment of HCV infection. MK-8742 has broad, potent HCV genotypic activity in vitro against viral variants that are resistant to other NS5A inhibitors. MK-8742 exhibits potent antiviral activity during 5 days of monotherapy in patients with GT1 and GT3 chronic HCV infection. MK-8742 is currently in Phase IIB development.
http://www.natap.org/2012/EASL/EASL_46.htm
………………
http://www.google.com/patents/WO2012040923A1?cl=en
EXAMPLE 23
Preparation of Compound A
A mixture of Compound Int-19b (1.1 g, 3 mmol), (dibromomethyl)benzene (2.25 g, 9 mmol) and K2C03 (1.2 g, 9 mmol) in 15 mL of DMF was heated to 100 °C and allowed to stir at this temperature for 3 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, concentrated in vacuo and the residue obtained was dissolved with
dichloromethane and water. The aqueous phase was extracted with dichloromethane. The combined organic extracts were washed with brine, dried over Na2S04, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. The resulting residue was purified using flash column
chromatography on silica gel to provide Compound Int-23a (380 mg, 28 %) as a white solid. 1H MR (CDCI3): δ 7.72 (bs, 1 H), 7.44 – 7.46 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1 H), 7.21 – 7.28 (m, 3 H), 7.09 – 7.12 (m, 3 H), 7.04 (s, 1 H), 6.99 – 7.01 (bs, J= 6.8 Hz, 2 H), 6.78 (s, 1 H), 6.63 – 6.65 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H). MS (ESI)
m/e (M+H+): 456. Step B – Pre aration of Compound Int-23b
lnt-23a lnt-23b
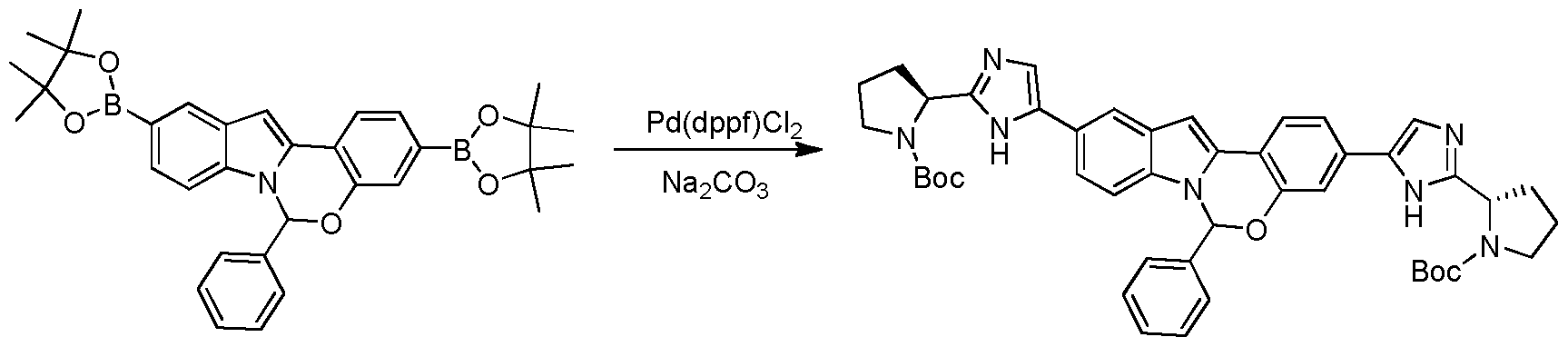
To a solution of Int-23a (456 mg, 1.0 mmol) in 1,4-dioxane was added bis pinacol borate (2.2 mmol) , Pd(dppf)Cl2 (0.04 mmol) and KOAc (4 mmol). The reaction mixture was put under N¾ heated to 110°C and allowed to stir at this temperature for 3 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, concentrated in vacuo, and the residue obtained was purified using column chromatography on silica gel to provide Compound Int- 23b (590 mg, 87 % yield). 1H MR (CDC13): δ 8.13 (s, 1 H), 7.60 (d, J= 7.6 Hz, 1 H), 7.52 (d, J= 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.36 – 7.39 (m, 1 H), 7.14 -7.19 (m, 4 H), 6.93 – 6.95 (m, 3 H), 6.90 (s, 1 H), 1.26 – 1.29 (s, 24 H). MS (ESI) m / e (M+H+): 550.
- Pre aration of Compound Int-23c
lnt-23b lnt-23c
A suspension of Int-23b (550 mg, 1.0 mmol), tert-butyl 2-(2-bromo-lH- imidazol-5-yl) pyrrolidine- 1-carboxylate (2.4 mmol), Pd(dppf) Cl2 (200 mg), Na2C03 (3 mmol) and in THF/H20 (10: 1, 33 mL) was allowed to stir at reflux for about 15 hours under N2. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and filtered, and the filtrate was washed with water (50 mL) and extracted with EtOAc (100 mL). The organic extract was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. The resulting residue was purified using column chromatography on silica gel to provide Compound Int-23c (160 mg). MS (ESI) m / e (M+H+): 768.
Preparation of Compound Int-23d
Int-23c (0.10 g, 0.13 mmol) was added to HCl/CH3OH (5 mL, 3M) and the resulting reaction was allowed to stir at room temperature for about 3 hours. The reaction mixture was then concentrated in vacuo to provide Compound Int-23d, which was used without further purification. MS (ESI) m / e (M+H+): 568.
- Preparation of Compound A
To a solution of Int-23d (56.8 mg, 0.10 mmol), (S)-2- (methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoic acid (35.0 mg, 0.20 mmol) and DIPEA (0.8 mmol) in CH3CN (1 mL) was added BOP (98 mg, 0.22 mmol). The resulting reaction was allowed to stir at room temperature and monitored using LCMS. After LCMS showed the starting material to be consumed, the reactionmixture was filtered, and the filtrate was purified using HPLC to provide Compound A as a white solid. 1H MR (MeOD): δ 7.94 (s,
1 H), 7.85 (d, J= 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 7.74 (s, 1 H), 7.63 (s, 1 H), 7.48 (s, 1 H), 7.35 – 7.37 (m, 2 H), 7.31 (s, 1 H), 7.17 – 7.18 (m, 4 H), 7.11 (s, 1 H), 6.96 – 6.98 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2 H), 5.09 – 5.17
(m, 2 H), 4.13 (t, J= 8.0 Hz, 2 H), 3.99 (bs, 2 H), 3.78 (bs, 2 H), 3.56 (s, 6 H), 2.44 – 2.47 (m,
2 H), 1.92 – 2.19 (m, 8 H), 0.77 – 0.85 (m, 12 H). MS (ESI) m / e (M+H+): 882.
The diastereomers were separated on a chiral SFC column: Isomer A: 1H NMR (MeOD): δ 8.08 (s, 1H), 7.91 – 7.93 (m, 1 H), 7.72 (s, 1 H), 7.56 (s, 1 H), 7.24 – 7.43 (m, 7 H), 7.19 (s, 1 H), 7.03 – 7.05 (m, 2 H), 5.16 – 5.24 (m, 2 H), 3.81 – 4.21 (m, 6 H), 3.62 (s, 6 H), 2.52 – 2.54 (m, 2 H), 2.00 – 2.25 (m, 8 H), 0.84 – 0.91 (m, 12 H). MS (ESI) m/z (M+H)+: 882.
Isomer B: 1H NMR (MeOD): δ 7.90 (s, 1 H), 7.81 – 7.83 (m, 1 H), 7.72 (s, 1 H), 7.62 (s, 1 H), 7.45 (s, 1 H), 7.14 – 7.33 (m, 6 H), 7.09 (s, 1 H), 6.93 – 6.95 (m, 2 H), 5.06 – 5.14 (m, 2 H), 3.71 – 4.11 (m, 6 H), 3.52 (s, 6 H), 2.41 – 2.44 (m, 2 H), 1.90 – 2.15 (m, 8 H), 0.74 – 0.86 (m, 12 H). MS (ESI) m/z (M+H)+: 882.

……………………..
Discovery of MK-8742: An HCV NS5A inhibitor with broad genotype activity
ChemMedChem 2013, 8(12): 1930
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cmdc.201300343/abstract
The NS5A protein plays a critical role in the replication of HCV and has been the focus of numerous research efforts over the past few years. NS5A inhibitors have shown impressive in vitro potency profiles in HCV replicon assays, making them attractive components for inclusion in all oral combination regimens. Early work in the NS5A arena led to the discovery of our first clinical candidate, MK-4882 [2-((S)-pyrrolidin-2-yl)-5-(2-(4-(5-((S)-pyrrolidin-2-yl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl)phenyl)benzofuran-5-yl)-1H-imidazole]. While preclinical proof-of-concept studies in HCV-infected chimpanzees harboring chronic genotype 1 infections resulted in significant decreases in viral load after both single- and multiple-dose treatments, viral breakthrough proved to be a concern, thus necessitating the development of compounds with increased potency against a number of genotypes and NS5A resistance mutations. Modification of the MK-4882 core scaffold by introduction of a cyclic constraint afforded a series of tetracyclic inhibitors, which showed improved virologic profiles. Herein we describe the research efforts that led to the discovery of MK-8742, a tetracyclic indole-based NS5A inhibitor, which is currently in phase 2b clinical trials as part of an all-oral, interferon-free regimen for the treatment of HCV infection.
see
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (2014), 57(5), 1643-1672.
| WO2010111483A1 * | Mar 25, 2010 | Sep 30, 2010 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Inhibitors of hepatitis c virus replication |
| US20070049593 * | Feb 23, 2005 | Mar 1, 2007 | Japan Tobacco Inc. | Tetracyclic fused heterocyclic compound and use thereof as HCV polymerase inhibitor |
Filed under: Breakthrough Therapy Designation, Phase2 drugs, Uncategorized Tagged: Anti-Hepatitis C Virus, Breakthrough Therapy Designation, Elbasvir, MK 8742, phase 2