AMPRENAVIR
Amprenavir (Agenerase, GlaxoSmithKline) is a protease inhibitor used to treat HIV infection. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on April 15, 1999, for twice-a-day dosing instead of needing to be taken every eight hours. The convenient dosing came at a price, as the dose required is 1,200 mg, delivered in eight very large gel capsules.
Production of amprenavir was discontinued by the manufacturer December 31, 2004; a prodrug version (fosamprenavir) is available.
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
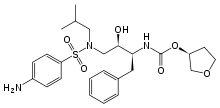
| (3S)-oxolan-3-yl N-[(2S,3R)-3-hydroxy-4-[N-(2-methylpropyl)(4-aminobenzene)sulfonamido]-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Agenerase |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a699051 |
| Licence data | EMA:Link, US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy cat. | C (US) |
| Routes | oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Half-life | 7.1-10.6 hours |
| Excretion | <3% renal |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 161814-49-9  |
| ATC code | J05AE05 |
| PubChem | CID 65016 |
| DrugBank | DB00701 |
| ChemSpider | 58532  |
| UNII | 5S0W860XNR  |
| KEGG | D00894  |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:40050  |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL116  |
| NIAID ChemDB | 006080 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C25H35N3O6S |
| Mol. mass | 505.628 g/mol |
Amprenavir (Agenerase, GlaxoSmithKline) is a protease inhibitor used to treat HIV infection. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on April 15, 1999, for twice-a-day dosing instead of needing to be taken every eight hours. The convenient dosing came at a price, as the dose required is 1,200 mg, delivered in eight very large gel capsules.
Production of amprenavir was discontinued by the manufacturer December 31, 2004; a prodrug version (fosamprenavir) is available
………………….
New approaches to the industrial synthesis of HIV protease inhibitors
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2004/ob/b404071f/unauth#!divAbstract
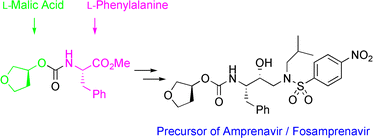
Efficient and industrially applicable synthetic processes for precursors of HIV protease inhibitors (Amprenavir, Fosamprenavir) are described. These involve a novel and economical method for the preparation of a key intermediate, (3S)-hydroxytetrahydrofuran, from L-malic acid. Three new approaches to the assembly of Amprenavir are also discussed. Of these, a synthetic route in which an (S)-tetrahydrofuranyloxy carbonyl is attached to L-phenylalanine appears to be the most promising manufacturing process, in that it offers satisfactory stereoselectivity in fewer steps.
AGENERASE (amprenavir) is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease. The chemical name of amprenavir is (3S)-tetrahydro-3-furyl N-[(1S,2R)-3-(4-amino-N-isobutylbenzenesulfonamido)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxypropyl]carbamate. Amprenavir is a single stereoisomer with the (3S)(1S,2R) configuration. It has a molecular formula of C25H35N3O6S and a molecular weight of 505.64. It has the following structural formula:
 |
Amprenavir is a white to cream-colored solid with a solubility of approximately 0.04 mg/mL in water at 25°C.
AGENERASE Capsules (amprenavir capsules) are
available for oral administration. Each 50- mg capsule contains the inactive ingredients d-alpha tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS), polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400) 246.7 mg, and propylene glycol 19 mg. The capsule shell contains the inactive ingredients d-sorbitol and sorbitans solution, gelatin, glycerin, and titanium dioxide. The soft gelatin capsules are printed with edible red ink. Each 50- mg AGENERASE Capsule contains 36.3 IU vitamin E in the form of TPGS. The total amount of vitamin E in the recommended daily adult dose of AGENERASE is 1,744 IU.
See also
- Fosamprenavir, a prodrug of amprenavir
External links
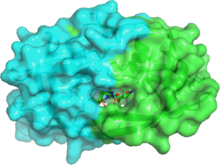
- Amprenavir bound to proteins in the PDB
Filed under: GENERIC DRUG, Uncategorized Tagged: Agenerase, amprenavir, Food and Drug Administration, GlaxoSmithKline, HIV infection, HIV protease inhibitors, protease inhibitor