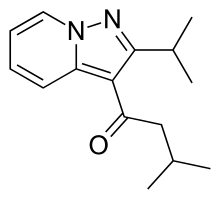
IBUDILAST
AV-411
KC-404
MN-166
2-methyl-1-(2-propan-2-ylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)propan-1-one
KYORIN Kyorin Seiyaku Kk……….INNOVATOR

Ibudilast is an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective oral agent which shows an excellent safety profile at 60 mg/day and provides significantly prolonged time-to-first relapse and attenuated brain volume shrinkage in patients with relapsing-remitting (RR) and/or secondary progressive (SP) multiple sclerosis (MS). Ibudilast is currently in development in the U.S. (codes: AV-411 or MN-166), but is approved for use as an antiinflammatory in Japan.



Ibudilast (development codes: AV-411 or MN-166) is an antiinflammatory drug used mainly in Japan, which acts as aphosphodiesterase inhibitor, inhibiting the PDE-4 subtype to the greatest extent,[1] but also showing significant inhibition of other PDE subtypes.[2][3]
Ibudilast has bronchodilator, vasodilator [4] and neuroprotective effects,[5][6] and is mainly used in the treatment of asthma andstroke.[7] It inhibits platelet aggregation,[8] and may also be useful in the treatment of multiple sclerosis.[9]
Ibudilast crosses the blood–brain barrier and suppresses glial cell activation. This activity has been shown to make ibudilast useful in the treatment of neuropathic pain and it not only enhances analgesia produced by opioid drugs, but also reduces the development oftolerance.[10]
![]()
It may have some use reducing methamphetamine addiction.[11]
Avigen has identified the potential of ibudilast (AV-411) for the treatment of neuropathic pain and other neurological indications, including opiate withdrawal. As an inhibitor of glial cells, ibudilast can deactivate these cells which produce various chemicals, including proinflammatory cytokines, in response to nerve damage or viral infection to amplify and maintain pain. Preclinical evaluation to date indicates that it reverses the painful sensory abnormality allodynia in chemotherapy- and trauma-induced neuropathic pain models.
Originator Kyorin and Banyu Pharmaceutical (now MSD KK following the merger of Banyu and Schering-Plough KK in 2010) have been developing ibudilast under a collaborative agreement. MediciNova obtained exclusive, worldwide rights outside of Japan, China, Taiwan and South Korea from Kyorin in October 2004 to develop and commercialize the compound for MS. In 2012, a codevelopment agreement was signed between MediciNova and the University of Colorado for the treatment of post-traumatic brain injury.

Sixteenth revised Japanese Pharmacopoeia chemicals, etc. IBUDILAST Ibudilast C14H18N2O: 230.31 [ 50847-11-5 ] that this product was dried when to quantify, including ibudilast (C14H18N2O) 98.5 ~ 101.0%.

 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
| 2-methyl-1-(2-propan-2-ylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)propan-1-one | |
| Clinical data | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 50847-11-5  |
| ATC code | R03DC04 |
| PubChem | CID 3671 |
| DrugBank | DB05266 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C14H18N2O |
| Mol. mass | 230.31 g/mol |
……………………………
http://www.google.co.in/patents/US3850941
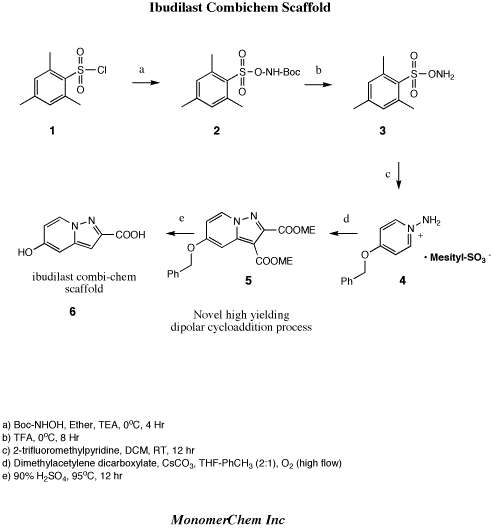
EXAMPLE 1 Synthesis of 2-isopropyl-3-is0butyrylpyrazolo[1,5-a] pyridine (KC404) A mixture of 1-amino-Z-methylpyridinium iodide g.), isobutyric anhydride (500 g.) and K CO (81 g.) was refluxed for 8 hr. After cooling, the precipitated crystals were filtered off and water was added to the filtrate, The solution was made basic to pH 11 with K CO’ and extracted with ethyl acetate (1000 ml.). The extract’was washed with water (400 ml.), dried over Na SO and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was distilled to give 58 g. of colorless crystalline product, hp, 110- 175 (7.5 mm. Hg). Recrystallization from hexane gave colorless prisms, melting point 53.554.
Analysis- Calcd.: C, 73.01; H, 7.88; N, 12.17 Found: C, 72.86; H, 7.94; N, 12.09
………………………………………..
http://www.customsynthesis.com/ibud.html
………………………..
http://www.google.com/patents/US8119657
FIG. 6 is a synthetic reaction scheme illustrating one approach for preparing (S)-AV1013; the approach employs chiral chromatography of an N-protected form of the racemate as described in detail in Example 1.
FIG. 7 demonstrates additional reaction schemes for synthesizing (S)-AV1013.


Example 1Synthesis of (S)-2-amino-1-(2-isopropylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)propan-1-one hydrochloride
(S)-2-Amino-1-(2-isopropylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)propan-1-one hydrochloride (also referred to herein as S-AV1013.HCl) was prepared on a preparative scale using two different routes to obtain the intermediate isopropylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine (IPPP). In the first approach (method 1), ibudilast was employed as the starting material to obtain IPPP; an alternate synthetic approach (method 2) employed ibudilast acid as the starting material.
Step 1Method 1Preparation of Isopropylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine (IPPP) from ibudilast
A 5 L 3-neck round-bottom flask was equipped with a mechanical stirrer, thermocouple, heating mantle and a Y-adapter with a nitrogen inlet. The flask was charged with water (350 mL, USP), concentrated sulfuric acid (350 mL) and ibudilast (3-isobutyryl-2-isopropylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine) (140 g, 0.608 mol). The flask was purged with nitrogen, and the mixture was stirred while it was heated to 135° C. An aliquot was removed for HPLC analysis, which showed that all starting material was consumed after 5 hours at 135° C., so the mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature overnight. The mixture was cooled in an ice bath, and water (1400 mL, USP) was added over 10 min, with the temperature maintained below 25° C. With continuous cooling in an ice bath, the mixture was neutralized by adding sodium hydroxide (50% w/w aq., 1150 mL) dropwise, with the temperature maintained below 25° C. Ethyl acetate (250 mL) was added, and the layers were separated. The aqueous layer was washed with ethyl acetate (2×300 mL). The combined ethyl acetate extracts were washed sequentially with 250 mL portions of saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate and saturated aqueous sodium chloride, then dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate for 30 minutes. Activated carbon (20 g) and silica (60 g) were added and stirred before filtering over a pad of Celite. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain 96.5 g of IPPP (2-isopropyl-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine, 99% crude yield, 99.6 area % pure by HPLC) as an amber oil.
1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ 1.4 (d, 6H), 3.2 (m, 1H), 6.3 (s, 1H), 6.6 (t, 1H), 7.0 (m, 1H), 7.4 (d, 1H), 8.4 (d, 1H). HPLC: RT=9.1 min (99.6 area %).
………………………………………..
Ibudilast (3-isobutyryl-2-isopropylpyrazolo[l,5-α]pyridine) is a small molecule drug that has been used for many years in Japan and Korea for the treatment of bronchial asthma as well as for treatment of cerebrovascular disorders such as post-stroke dizziness. It is sold in these countries under the tradename, Ketas®. Marketed indications for ibudilast in Japan include its use as a vasodilator, for treating allergy, eye tissue regeneration, ocular disease, and treatment of allergic ophthalmic disease (Thompson Current Drug Reports). Its use in the treatment of both chronic brain infarction (ClinicalTrials.gov) and multiple sclerosis (News.Medical.Net; Pharmaceutical News, 2 Aug 2005) is currently being explored in separate, ongoing clinical trials.
The mechanisms of action of ibudilast have been widely explored. Its role as a non-selective inhibitor of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) has been described
(Fujimoto, T., et al., J. of Neuroimmunology, 95 (1999) 35-92). Additionally, ibudilast has been reported to act as an LTD4 antagonist, an anti-inflammatory, a PAF antagonist, and a vasodilatator agent (Thompson Current Drug Reports). Ibudilast is also thought to exert a neuroprotective role in the central nervous system of mammals, presumably via suppression of the activation of glial cells (Mizuno et al. (2004) Neuropharmacology 46: 404-411). New uses for ibudilast continue to be explored.http://www.google.com/patents/WO2007146087A2?cl=en
…………………………
http://www.google.com/patents/WO2007142924A1?cl=en
IBUDILAST
Ibudilast is a small molecule drug (molecular weight of 230.3) having the structure shown below.
Ibudilast is also found under ChemBank ID 3227, CAS # 50847-1 1-5, and Beilstein Handbook Reference No. 5-24-03-00396. Its molecular formula corresponds to [Ci4HIgN2O]. Ibudilast is also known by various chemical names which include 2- methyl-l-(2-(l-methylethyI)pyrazolo(l,5-a)pyridin-3-yl)l-propanone; 3-isobutyryl-2- isopropylpyrazolo(l,5-a)pyridine]; and l-(2-isopropyl-pyrazolo[l,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-2- methyl-propan-1-one. Other synonyms for ibudilast include Ibudilastum (Latin), BRN 0656579, KC-404, and the brand name Ketas®. Ibudilast, as referred to herein, is meant to include any and all pharmaceutically acceptable salt forms thereof, prodrug forms (e.g., the corresponding ketal), and the like, as appropriate for use in its intended formulation for administration.
Ibudilast is a non-selective nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor (most active against PDE-3 and PDE-4), and has also been reported to have LTD4 and PAF antagonistic activities. Its profile appears effectively anti-inflammatory and unique in comparison to other PDE inhibitors and anti-inflammatory agents. PDEs catalyze the hydrolysis of the phosphoester bond on the 3 ‘-carbon to yield the corresponding 5′- nucleotide monophosphate. Thus, they regulate the cellular concentrations of cyclic nucleotides. Since extracellular receptors for many hormones and neurotransmitters utilize cyclic nucleotides as second messengers, the PDEs also regulate cellular responses to these extracellular signals. There are at least eight classes of PDEs: Ca2+/calmodul in-dependent PDEs (PDEl); cGMP-stimulated PDEs (PDE2); cGMP- inhibited PDEs (PDE3); cAMP-specific PDEs (PDE4); cGMP-binding PDEs (PDE5); photoreceptor PDEs (PDE6); high affinity, cAMP-specific PDEs (PDE7); and high affinity cGMP-specific PDEs (PDE9).
References
- Huang Z, Liu S, Zhang L, Salem M, Greig GM, Chan CC, Natsumeda Y, Noguchi K. Preferential inhibition of human phosphodiesterase 4 by ibudilast. Life Sciences. 2006 May 1;78(23):2663-8.
- Suzumura A, Ito A, Yoshikawa M, Sawada M. Ibudilast suppresses TNFalpha production by glial cells functioning mainly as type III phosphodiesterase inhibitor in the CNS. Brain Research. 1999 Aug 7;837(1-2):203-12.
- Gibson LC, Hastings SF, McPhee I, Clayton RA, Darroch CE, Mackenzie A, Mackenzie FL, Nagasawa M, Stevens PA, Mackenzie SJ. The inhibitory profile of Ibudilast against the human phosphodiesterase enzyme family. European Journal of Pharmacology. 2006 May 24;538(1-3):39-42.
- Kishi Y, Ohta S, Kasuya N, Sakita S, Ashikaga T, Isobe M. Ibudilast: a non-selective PDE inhibitor with multiple actions on blood cells and the vascular wall. Cardiovascular Drug Reviews. 2001 Fall;19(3):215-25.
- Mizuno T, Kurotani T, Komatsu Y, Kawanokuchi J, Kato H, Mitsuma N, Suzumura A. Neuroprotective role of phosphodiesterase inhibitor ibudilast on neuronal cell death induced by activated microglia. Neuropharmacology. 2004 Mar;46(3):404-11.
- Yoshioka M, Suda N, Mori K, Ueno K, Itoh Y, Togashi H, Matsumoto M. Effects of ibudilast on hippocampal long-term potentiation and passive avoidance responses in rats with transient cerebral ischemia. Pharmacological Research. 2002 Apr;45(4):305-11.
- Wakita H, Tomimoto H, Akiguchi I, Lin JX, Ihara M, Ohtani R, Shibata M. Ibudilast, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, protects against white matter damage under chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat. Brain Research. 2003 Nov 28;992(1):53-9.
- Rile G, Yatomi Y, Qi R, Satoh K, Ozaki Y. Potentiation of ibudilast inhibition of platelet aggregation in the presence of endothelial cells. Thrombosis Research. 2001 May 1;102(3):239-46.
- Feng J, Misu T, Fujihara K, Sakoda S, Nakatsuji Y, Fukaura H, Kikuchi S, Tashiro K, Suzumura A, Ishii N, Sugamura K, Nakashima I, Itoyama Y. Ibudilast, a nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitor, regulates Th1/Th2 balance and NKT cell subset in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis. 2004 Oct;10(5):494-8.
- Ledeboer A, Hutchinson MR, Watkins LR, Johnson KW. Ibudilast (AV-411). A new class therapeutic candidate for neuropathic pain and opioid withdrawal syndromes. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 2007 Jul;16(7):935-50.
- http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2013/04/03/meth-addiction-cure-ucla-ibudilast_n_2863126.html?utm_hp_ref=mostpopular#slide=more268305
Literature References:
Leukotriene D4 antagonist. Prepn: T. Irikura et al., DE 2315801; eidem, US 3850941 (1973, 1974 both to Kyorin).
Pharmacology and antiallergic activity: K. Nishino et al., Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 33, 267 (1983); H. Nagai et al., ibid. 1215.
In vitro cerebral vasodilating activity: M. Ohashi et al., Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. 280, 216 (1986);
in vivo activity: W. M. Armstead et al., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 244, 138 (1988).
Bronchodilating activity in animals: S. Mue et al., Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. 283,153 (1986).
Antiplatelet activity in animals: M. Ohashi et al., ibid. 321; M. Ohashi et al., Gen. Pharmacol. 17, 385 (1986).

| Patent | Filing date | Publication date | Applicant | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4097483 | Aug 31, 1976 | Jun 27, 1978 | Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Pyrazolo 1,5-a!pyridines |
| US7585875 * | Jun 6, 2007 | Sep 8, 2009 | Avigen, Inc. | Phosphodiesterase inhibitors; neuropathic pain, inflammation, opioid dependence or withdrawal; 2-amino-1-(2-isopropylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)propan-1-one for example |
| US20070015924 | Jun 15, 2006 | Jan 18, 2007 | Cardiome Pharma Corp. | stereoselective preparation of aminocyclohexyl ether compounds such as trans-(1R,2R)-aminocyclohexyl ether compounds and/or trans-(1S,2S)-aminocyclohexyl ether compounds; useful in treating arrhythmias |
| US20080070912 | Jun 6, 2007 | Mar 20, 2008 | Avigen, Inc. | Phosphodiesterase inhibitors; neuropathic pain, inflammation, opioid dependence or withdrawal; 2-amino-1-(2-isopropylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)propan-1-one for example |
| US20090062330 | Jul 8, 2008 | Mar 5, 2009 | Medicinova, Inc. | Treatment of progressive neurodegenerative disease with ibudilast |
| US20090318437 * | Jun 10, 2009 | Dec 24, 2009 | Gaeta Federico C A | SUBSTITUTED PYRAZOLO[1,5-a] PYRIDINE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE |
| WO2007142924A1 | May 29, 2007 | Dec 13, 2007 | Avigen Inc | Ibudilast for inhibiting macrophage migration inhibitory factor (mif) activity |
| WO2007146087A2 * | Jun 6, 2007 | Dec 21, 2007 | Avigen Inc | SUBSTITUTED PYRAZOLO [1,5-α] PYRIDINE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR METHODS OF USE |
| WO2010151551A1 * | Jun 22, 2010 | Dec 29, 2010 | Medicinova, Inc. | ENANTIOMERIC COMPOSITIONS OF 2-AMINO-1-(2-ISOPROPYLPYRAZOLO[1,5-a]PYRIDIN-3-YL)PROPAN-1-ONE AND RELATED METHODS |
| US8119657 | Jun 22, 2010 | Feb 21, 2012 | Medicinova, Inc. | Enantiomeric compositions of 2-amino-1-(2-isopropylpyrazolo[1,5-α]pyridin-3-yl)propan-1-one and related methods |
| Patent | Filing date | Publication date | Applicant | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2003104178A1 * | Jun 6, 2003 | Dec 18, 2003 | Cortical Pty Ltd | Napththalene derivatives which inhibit the cytokine or biological activity of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (mif) |
| WO2003104203A1 * | Jun 6, 2003 | Dec 18, 2003 | Cortical Pty Ltd | Therapeutic molecules and methods-1 |
| WO2004058713A1 * | Dec 18, 2003 | Jul 15, 2004 | Jason Chyba | Differential tumor cytotoxocity compounds and compositions |
| WO2005058304A1 * | Dec 17, 2004 | Jun 30, 2005 | Cortical Pty Ltd | Implantable device containing inhibitor of macrophage migration inhibitory factor |
| WO2006045505A1 * | Oct 19, 2005 | May 4, 2006 | Novartis Ag | Mif-inhibitors |
| WO2006108671A1 * | Apr 13, 2006 | Oct 19, 2006 | Novartis Ag | 3,4-dihydro-benzo[e][1,3]oxazin-2-ones |
Keywords: Antiallergic; Antiasthmatic (Nonbronchodilator); Leukotriene Antagonist; Vasodilator (Cerebral).

Filed under: Uncategorized Tagged: Antiallergic, Antiallergic; antiasthmatic; vasodilator, Antiasthmatic, ibudilast, KC 404, KYORIN, Leukotriene Antagonist



