
TOSEDOSTAT
An aminopeptidase inhibitor with antineoplastic activity.
- CHR 2797
- CHR-2797
- Tosedostat
- UNII-KZK563J2UW
- BB-76163Vernalis (Originator)
| CAS No. | 238750-77-1 |
| Chemical Name: | Tosedostat |
| Synonyms: | BB-76163;Chr-2797;tosedostat;CHR2797 (Tosedostat);Tosedostat (CHR2797);α-[[(2R)-2-[(1S)-1-Hydroxy-2-(hydroxyamino)-2-oxoethyl]-4-methyl-1-oxopentyl]amino]-benzeneaceticacidcyclopentlyester;alpha-[[(2R)-2-[(1S)-1-Hydroxy-2-(hydroxyamino)-2-oxoethyl]-4-methyl-1-oxopentyl]amino]benzeneacetic acid cyclopentyl ester;Benzeneacetic acid, alpha-(((2R)-2-((1S)-1-hydroxy-2-(hydroxyamino)-2-oxoethyl)-4-methyl-1-oxopentyl)amino)-, cyclopentyl ester, (alphas)- |
| Molecular Formula: | C21H30N2O6 |
| Formula Weight: | 406.47 |
CHR-2797 is an oral, once-daily experimental cancer therapy in phase II clinical development at Chroma Therapeutics for the oral treatment of refractory acute myeloid leukemia in elderly patients. It is also in early clinical development for the treatment of refractory solid tumors alone or in combination with chemotherapy.
No recent development has been reported for phase I/II studies evaluating CHR-2797 as monotherapy in hematologic/blood cancer. A phase I/II clinical trial of the compound in combination with erlotinib for non-small cell lung cancer was terminated in 2010 due to very poor recruitment of patients to the study.
Cell Therapeutics is also conducting phase II clinical trials of the compound for the treatment of myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia.
CHR- 2797 is an inhibitor of aminopeptidases and has demonstrated strong preclinical efficacy as monotherapy in addition to demonstrating strong synergy with a number of leading cancer therapies in a range of cancer cells. It was originally licensed from Vernalis, where it was being evaluated for its potential in treating multiple sclerosis; however development in this indication has been discontinued.
In 2008, orphan drug designation was assigned to CHR-2797 in the U.S. for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. In 2011, the compound was licensed to Cell Therapeutics by Chroma Therapeutics in Central America, North America and South America for exclusive marketing and codevelopment for the oral treatment of blood-related cancers and other cancers.
In corporate news, biopharmaceutical company Cell Therapeutics, Inc. (CTIC) was up more than 6% and near 52 week highs after saying Thursday that the U.S. FDA has removed the partial clinical hold on tosedostat and all studies underway have been allowed to continue. Tosedostat is under development for the treatment of blood-related cancers. It is currently being studied in Phase 2 trials in elderly patients with newly diagnosed and relapsed acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes.
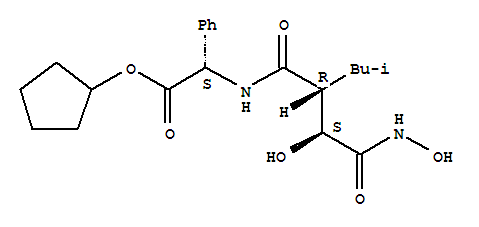
Tosedostat is a proprietary orally bioavailable inhibitor of the M1 family of aminopeptidases with potential antineoplastic activity.
Tosedostat is converted intracellularly into a poorly membrane-permeable active metabolite (CHR-79888) which inhibits the M1 family of aminopeptidases, particularly puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase (PuSA), and leukotriene A4 (LTA4) hydrolase; inhibition of these aminopeptidases in tumor cells may result in amino acid deprivation, inhibition of protein synthesis due to a decrease in the intracellular free amino acid pool, an increase in the level of the proapoptotic protein Noxa, and cell death.
Noxa is a member of the BH3 (Bcl-2 homology 3)-only subgroup of the proapoptotic Bcl-2 (B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2) protein family
Cell Therapeutics announced that it has received notification from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that the partial clinical hold on tosedostat (IND 075503) has been removed and all studies underway may continue. Tosedostat is a first-in-class selective inhibitor of aminopeptidases, which are required by tumor cells to provide amino acids necessary for growth and tumor cell survival, and is under development for the treatment of blood-related cancers.
Tosedostat is currently being studied in the United States and European Union in investigator-sponsored and cooperative group-sponsored Phase 2 trials in elderly patients with newly diagnosed and relapsed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
“We are pleased that the FDA has responded favorably to the tosedostat clinical trial data provided and removed the partial clinical hold to allow further development of tosedostat in ongoing and future studies,” said John Pagel, MD, PhD, Associate Member, Clinical Research Division, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center; Associate Professor, Medical Oncology Division, University of Washington School of Medicine; and Principal Investigator in the tosedostat first-line AML/MDS trial.
Recently, WO 93/20047 disclosed a class of hydroxamic acid based MMP inhibitors which also are active in inhibiting TNF production.
As mentioned above, MMP inhibitors have been proposed with hydroxamic acid or carboxylic acid zinc binding groups. The following patent publications disclose hydroxamic acid-based MMP inhibitors:
US 4599361 (Searle) EP-A-0236872 (Roche) EP-A-0274453 (Bellon) WO 90/05716 (British Bio-technology) WO 90/05719 (British Bio-technology) WO 91/02716 (British Bio-technology) EP-A-0489577 (Celltech) EP-A-0489579 (Celltech) EP-A-0497192 (Roche) WO 92/13831 (British Bio-technology) WO 92/17460 (SmithKline Beecham) WO 92/22523 – (Research Corporation Technologies) WO 93/09090 (Yamanouchi) WO 93/09097 (Sankyo) WO 93/20047 (British Bio-technology) WO 93/24449 (Celltech) WO 93/24475 (Celltech) EP-A-0574758 (Roche) The following patent publications disclose carboxylic acid-based MMP inhibitors:
EP-A-0489577 (Celltech) EP-A-0489579 (Celltech) WO 93/24449 (Celltech) WO 93/24475 (Celltech)
|
|
|
TOSEDOSTAT
| WO1996033166A1 * | 17 Apr 1996 | 24 Oct 1996 | Du Pont Merck Pharma | Hydroxamic and carboxylic acids as metalloprotease inhibitors |
| WO1998011063A1 * | 8 Sep 1997 | 19 Mar 1998 | British Biotech Pharm | Cytostatic hydroxamic acid derivatives |
| GB2268934A * | Title not available |
| US5652262 * | 14 mar 1994 | 29 lug 1997 | British Biotech Pharmaceutical, Ltd. | Hydroxamic acid derivatives as metalloproteinase inhibitors |
| US5821262 * | 4 ott 1994 | 13 ott 1998 | British Biotech Pharmaceuticals Limited | Hydroxamic acid derivatives as inhibitors of cytokine production |
| US5861436 * | 29 apr 1997 | 19 gen 1999 | British Biotech Pharmaceuticals Limited | Hydroxamic acid derivatives as metalloproteinase inhibitors |
| EP0423943A2 | 19 set 1990 | 24 apr 1991 | Beecham Group p.l.c. | Use of collagenase inhibitors in the treatment of demyelinating diseases, in particular multiple sclerosis |
| JPH03157372A | Titolo non disponibile | |||
| WO1997049674A1 | 20 giu 1997 | 31 dic 1997 | Francesca Abrate | Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors |
| WO1998011063A1 | 8 set 1997 | 19 mar 1998 | British Biotech Pharm | Cytostatic hydroxamic acid derivatives |
| WO1999040910A1 | 27 gen 1999 | 19 ago 1999 | Andrew Paul Ayscough | Anti-inflammatory agents |
| WO1999044602A1 | 5 mar 1999 | 10 set 1999 | British Biotech Pharm | Inflammatory cell inhibitors |
| WO1999046241A1 | 12 mar 1998 | 16 set 1999 | British Biotech Pharm | Cytostatic agents |
| WO2000044373A1 * | Jan 27, 2000 | Aug 3, 2000 | Raymond Paul Beckett | Antibacterial hydroxamic acid derivatives |
| US6545051 | Jan 27, 2000 | Apr 8, 2003 | British Biotech Pharmaceuticals, Ltd. | Antibacterial hydroxamic acid derivatives |
Drugs Fut 2009, 34(2): 115
WO 1999046241
WO 1995019956
WO 1998011063
NMR
http://file.selleckchem.com/downloads/nmr/S152202-CHR-2797-NMR-Selleck.pdf
Anti-Metastatic and Anti-Invasive Agents Compounds which have the property of inhibiting the action of the metalioproteinase enzymes involved in connective tissue breakdown and remodelling, such as fibroblast collagenase (Type 1 ), PMN-collagenase, 72 kDa-gelatinase, 92 kDa- gelatinase, stromelysin, stromelysin-2 and PUMP-1 (known as “matrix metalloproteinases”, and herein referred to as MMPs) have been proposed and are being tested in the clinic for the treatment of solid tumours. Cancer cells are particularly adept at utilising the MMPs to achieve rapid remodelling of the extracellular matrix, thereby providing space for tumour expansion and permitting metastasis. MMP inhibitors should minimise these processes and thus slow or prevent cancer progression.
In view of the rapid emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria, the development of antibacterial agents with novel modes of action that are effective against the growing number of resistant bacteria, particularly the vancomycin resistant enterococci and β-lactam antibiotic-resistant bacteria, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylocccus aureus, is of utmost importance.
The natural antibiotic actinonin (see for example J. C. S Perkin I, 1975, 819) is a hydroxamic acid derivative of Structure (A):
In ddition to actinonin, various structural analogues of actinonin have also been shown to have antibacterial activity (see for example Broughton et al. (Devlin et al. Journal of the Chemical Society. Perkin Transactions 1 (9):830-841, 1975; Broughton et al. Journal of the Chemical Society. Perkin Transactions 1 (9):857-860, 1975).
The matlystatin group of compounds, share a number of structural similarities with actinonin. Both are peptidic molecules with functional hydroxamic acid metal binding groups (Ogita et al., J. Antibiotics. 45(11):1723-1732; Tanzawa et al., J. Antibiotics. 45(11):1733-1737; Haruyama et al., J. Antibiotics. 47(12):1473-1480; Tamaki et al., J. Antibiotics. 47(12):1481-1492).
Example 1
2-[2R-(S-Hydroxy-hydroxycarbamoyl-methyl)-4-methyl-pentanoylamine]-2-phenyl- ethanoic acid cyclopentyl ester
HO Ξ CONHOH
Prepared using procedures similar to those described in Preparative Example A using phenylglycine cyclopentyl ester.
Diastereoisomer A
Η-NMR; δ (MeOD), 7.4-7.29 (5H, m), 5.43 (1 H, s), 5.2-5.14 (1 H, m), 4.02 (1 H, d,
J=6.9Hz), 2.94-2.85 (1 H, m), 1.91-1.34 (10H, bm), 1.25-1.14 (1 H, m) and 0.86 (6H, 14 dd, J=6.5, 11.5Hz).
13C-NMR; δ (MeOD), 175.6, 171.8, 171.4, 137.8, 129.8, 129.4, 128.6, 80.0, 73.2,
58.5, 49.2, 39.1 , 33.3, 33.3, 26.8, 24.5, 24.4, 23.7 and 22.1.
Diastereoisomer B
Η-NMR; δ (MeOD), 7.33-7.19 (5H, m), 5.3 (1 H, s), 5.11-5.06 (1 H, m), 3.81 (1 H, d, J=7.3Hz), 2.83-2.74 (1 H, m), 1.83-1.45 (10H, bm), 1.12-1.03 (1 H, m) and 0.88-0.81 (6H, dd, J=6.4, 12.3Hz). 13C-NMR; δ (MeOD), 175.8, 171.8, 171.5, 137.3, 129.8, 129.5, 128.8, 79.9, 73.3, 58.7, 48.9, 39.2, 33.3, 33.3, 26.7, 24.5, 24.5, 24.0 and 22.2.
tosedostat
http://www.google.it/patents/US6545051

42
| WO98/11063 | WO99/46241 ex 1b | WO 98/11063 analogy ex 8 |

43
| WO98/11063 | WO99/46241 ex 1a | WO 98/11063 analogy ex 8 |
……………………………………………………………………
entry 65 in http://www.google.com/patents/WO2000044373A1
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
http://www.google.com/patents/WO1999044602A1
Example 43
2-[2R-(S-Hydroxy-hydroxycarbamoyl-methyl)-4-methyl-pentanoylamine]-2-phenyl- ethanoic acid cyclopentyl ester
TC
HO Ξ CONHOH
Prepared using procedures similar to those described in example 8 of WO 98/11063, using phenylglycine cyclopentyl ester.
Diastereoisomer A
1H-NMR; δ (MeOD), 7.4-7.29 (5H, m), 5.43 (1 H, s), 5.2-5.14 (1 H, m), 4.02 (1 H, d, 34
J=6.9Hz), 2.94-2.85 (1 H, m), 1.91-1.34 (10H, bm), 1.25-1.14 (1 H, m) and 0.86 (6H, dd, J=6.5, 11.5Hz).
13C-NMR; δ (MeOD), 175.6, 171.8, 171.4, 137.8, 129.8, 129.4, 128.6, 80.0, 73.2, 58.5, 49.2, 39.1 , 33.3, 33.3, 26.8, 24.5, 24.4, 23.7 and 22.1.
Diastereoisomer B
1H-NMR; δ (MeOD), 7.33-7.19 (5H, m), 5.3 (1 H, s), 5.11-5.06 (1 H, m), 3.81 (1 H, d,
J=7.3Hz), 2.83-2.74 (1 H, m), 1.83-1.45 (10H, bm), 1.12-1.03 (1 H, m) and
0.88-0.81 (6H, dd, J=6.4, 12.3Hz). 13C-NMR; δ (MeOD), 175.8, 171.8, 171.5, 137.3,
129.8, 129.5, 128.8, 79.9, 73.3, 58.7, 48.9, 39.2, 33.3, 33.3, 26.7, 24.5, 24.5, 24.0 and 22.2.
……………………………..
will be updated
Filed under: orphan drug status, phase2 drugs, Uncategorized Tagged: anthony crasto, medicinal chemistry, organic chemistry, Orphan Drug, phase 2, TOSEDOSTAT, world drug tracker




