
French drug maker Sanofi Tuesday said it has received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for its Priftin (rifapentine) tablets to treat latent tuberculosis infection, or LTBI.
Following a priority review, FDA has approved Priftin in combination with isoniazid, or INH, for a new indication for treatment of LTBI in patients two years of age and older at high risk of progression to tuberculosis or TB disease.
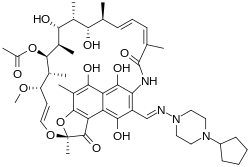
Rifapentine
Antibiotic DL 473IT;Cyclopentylrifampicin;DL 473;KTC 1;MDL 473;Prifitin;Priftin;R 77-3;Rifamycin AF/ACPP;
Rifapentine is an antibiotic drug used in the treatment of tuberculosis. It inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity in susceptible cells. Specifically, it interacts with bacterial RNA polymerase but does not inhibit the mammalian enzyme.
For the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis
3-(((4-Cyclopentyl-1-piperazinyl)imino)methyl)rifamycin
| C47H64N4O12 |
| 61379-65-5 |
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
| (7S,9E,11S,12R,13S,14R,15R,16R,17S,18S,19E,21Z,26E)-26-{[(4-cyclopentylpiperazin-1-yl)amino]methylidene}-2,15,17,29-tetrahydroxy-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22-heptamethyl-6,23,27-trioxo-8,30-dioxa-24-azatetracyclo[23.3.1.14,7.05,28]triaconta-1(28),2,4,9,19,21,25(29)-heptaen-13-yl acetate | |
| Clinical data | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a602026 |
| Legal status |
?
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | increases when administered with food |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 61379-65-5  |
| ATC code | J04AB05 |
| PubChem | CID 5462354 |
| DrugBank | DB01201 |
| ChemSpider | 10482075  |
| UNII | XJM390A33U  |
| KEGG | D00879  |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:45304  |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1660  |
| NIAID ChemDB | 007686 |
| Synonyms | 3{[(4-cyclopentyl-1-piperazinyl)imino]methyl}rifamycin |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C47H64N4O12 |
| Mol. mass | 877.031 g/mol |
Rifapentine (INN, marketed under the brand name Priftin by Sanofi-Aventis) is an antibiotic drug used in the treatment of tuberculosis.
Rifapentine was first synthesized in 1965 by the same company that produced rifampin. The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in June 1998.

Medical uses
A review of alternative regimens for prevention of active tuberculosis in HIV-negative individuals with latent TB found that a weekly, directly observed regimen of rifapentine with isoniazid for three months was as effective as a daily, self -administered regimen of isoniazid for nine months. But the rifapentine-isoniazid regimen had higher rates of treatment completion and lower rates of hepatotoxicity. However, the rate of treatment-limiting adverse events was higher in the rifapentine-isoniazid regimen. [1]
PRIFTIN (rifapentine) for oral administration contains 150 mg of the active ingredient rifapentine per tablet.
The 150 mg tablets also contain, as inactive ingredients: calcium stearate, disodium EDTA, FD&C Blue No. 2 aluminum lake, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose USP, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, pregelatinized starch, propylene glycol, sodium ascorbate, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium starch glycolate, synthetic red iron oxide, and titanium dioxide.
Rifapentine is a rifamycin derivative antibiotic and has a similar profile of microbiological activity to rifampin (rifampicin). The molecular weight is 877.04.
The molecular formula is C47H64N4O12.
The chemical name for rifapentine is rifamycin, 3-[[(4-cyclopentyl-1-piperazinyl)imino]methyl]-or 3-[N-(4-Cyclopentyl – 1-piperazinyl)formimidoyl] rifamycin or 5,6,9,17,19,21-hexahydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,18,20,22-heptamethyl-8-[N-(4-cyclopentyl-l-piperazinyl)-formimidoyl]-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienimino)naphtho[2,1-b]furan-1,11(2H)-dione 21-acetate. It has the following structure:
 |
Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Rifapentine has been assigned a Pregnancy Category C by the FDA. Rifapentine in pregnant women has not been studied, but animal reproduction studies have resulted in fetal harm and were teratogenic. If rifapentine and rifampin are used together in pregnancy, coagulation should be monitored due to a possible increased risk of maternal postpartum hemorrhage and infant bleeding. [2]
Adverse effects
Common side effects are hyperuricemia, pyuria, hematuria, urinary tract infection, proteinuria, neutropenia, anemia, and hypoglycemia. [2]
Contraindications
Rifapentine should be avoided in patients with an allergy to the rifamycin class of drugs. [2] This drug class includes rifampin and rifabutin. [3]
Interactions
Rifapentine induces metabolism by CYP3A4, CYP2C8 and CYP2C9 enzymes. It may be necessary to adjust the dosage of drugs metabolized by these enzymes if they are taken with rifapentine. Examples of drugs that may be affected by rifapentine include warfarin, propranolol, digoxin, protease inhibitors and oral contraceptives.[2]
History
Rifapentine was first synthesized in 1965 by the same company that produced rifampin. The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in June 1998. It is synthesized in one step from rifampicine.


Rifapentine was first synthesized in 1965 by the same company that produced rifampin. The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in June 1998.
(7S,11S,12S,13S,14R,15S,16R,17R,18R,26E)-26-{[(4-Cyclopentyl-1-piperazinyl)amino]methylene}-2,15,17,29-tetrahydroxy-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22-heptamethyl-6,23,27-trioxo-8,30-dioxa-24-azatetracyclo [23.3.1.14,7.05,28]triaconta-1(28),2,4,9,19,21,25(29)-heptaen-13-yl acetate. Rifapentine is an antibiotic drug used in the treatment of tuberculosis.
Preparation of Rifapentine: this chemical can be prepared by 3-aldehyde rifamycin SV with 1-Amino-4-cyclopentylpiperazine. This reaction needs reagent tetrahydrofuran. The yield is 55 %
References
- Sharma SK et al . (2013). “Rifamycins (rifampicin, rifabutin and rifapentine) compared to isoniazid for preventing tuberculosis in HIV-negative people at risk of active TB.”. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 7: CD007545. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007545.pub2. PMID 23828580.
- Sanofi-Aventis. (2010) Priftin (rifapentine): Highlights of Prescribing Information. Retrieved from http://products.sanofi.us/priftin/Priftin.pdf.
- CDC. (2013) Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/TB/education/corecurr/default.htm
- http://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/5/7/690/htm
Filed under: Uncategorized Tagged: Food and Drug Administration, rifapentine, SANOFI, tb, treatment of tuberculosis
